Laparoscopy surgery
Laparoscopicsurgery, also called minimally
invasive surgery (MIS),
bandaid surgery, or keyhole surgery, is a modern surgical technique.
There are a number of advantages to the patient with laparoscopic surgery
versus the more common, open procedure. These include reduced pain due to
smaller incisions, reduced hemorrhaging
and shorter recovery time. The key
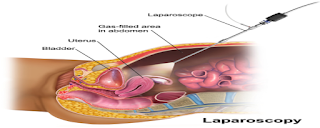
element is the use of a laparoscope, a long fibre optic cable system that allows viewing
of the affected area by snaking the cable from a more distant, but more easily
accessible location.
Laparoscopic surgery includes
operation within the abdomen or pelvic region .Laparoscopy can be used to help
diagnose a wide range of conditions that develop inside the abdomen or pelvis.
It can also be used to carry out surgical procedures, such as removing a
damaged or diseased organ, or removing a tissue sample for further testing
(biopsy).
Specific surgical instruments used
in a laparoscopic surgery include obstetrical
forceps, scissors, probes, dissectors,
hooks, and retractors. Laparoscopic and thoracoscopic surgery belong to the
broader field of endoscopy
In many cases, abdominal problems
can also be diagnosed with imaging techniques such as:
• ultrasound, which uses high-frequency sound
waves to create images of the body
• CT scan, which is a series of special X-rays that take cross-sectional images of
the body
• MRI scan, which uses magnets and radio
waves to produce images of the body
Laparoscopy is performed when these
tests don’t provide enough information or insight for a diagnosis. The
procedure may also be used to take a biopsy, or sample of tissue, from a
particular organ in the abdomen.


Comments
Post a Comment